ALS is a devastating disease that progressively affects the nerve cells responsible for controlling voluntary muscle movements. As these cells degenerate, individuals experience a gradual loss of muscle function, leading to a decline in their quality of life.
Understanding ALS
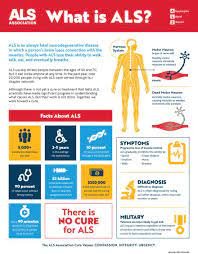
What is ALS?
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis is a complex disorder that involves the malfunction of motor neurons, the nerve cells responsible for transmitting signals from the brain to the muscles throughout the body. These motor neurons deteriorate over time, resulting in the muscles gradually losing their ability to function.
The Nervous System and Motor Neurons
The nervous system acts as the body’s communication network, transmitting signals between the brain and various body parts. Motor neurons play a crucial role in this system by transmitting commands from the brain to the muscles, enabling movements like walking, talking, and even breathing.
Symptoms of ALS
Early Signs and Manifestations
The initial symptoms of ALS can be subtle and often overlooked. These might include muscle twitches, cramps, or weakness in one limb. Gradually, these symptoms worsen and spread to other body parts.
Progressive Muscle Weakness
One of the hallmark symptoms of ALS is the progressive weakening of muscles. This can lead to difficulties in performing simple tasks like buttoning a shirt or lifting a cup. Over time, mobility becomes severely restricted.
Speech and Swallowing Difficulties
As the disease advances, muscles involved in speech and swallowing are also affected. Individuals with ALS may experience slurred speech and trouble swallowing food and liquids.
Causes and Risk Factors
Genetic Predisposition
Although most ALS cases are sporadic, a small percentage of cases are inherited due to specific genetic mutations. Mutations in genes such as C9orf72 and SOD1 have been linked to familial ALS.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to certain environmental toxins or traumatic injuries might contribute to the development of ALS. However, the exact relationship between these factors and the disease is still under investigation.
Diagnosis of ALS
Clinical Examination and Medical History
Diagnosing ALS can be challenging, as its symptoms can mimic those of other conditions. Physicians typically conduct a thorough clinical examination and consider the patient’s medical history to rule out other possibilities.
Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Conduction Studies
Electromyography and nerve conduction studies help measure the electrical activity in muscles and nerves. In ALS, abnormal patterns can provide valuable diagnostic information.
Treatment Approaches
Medications and Therapies
While there’s no cure for ALS, certain medications like Riluzole and Edaravone can help slow down its progression. Physical therapy and occupational therapy can also enhance mobility and quality of life.
Assistive Devices and Supportive Care
As muscle function declines, individuals often require assistive devices such as wheelchairs and communication devices. Palliative care and support from healthcare professionals become essential.
Ventilation Support
In later stages of ALS, respiratory muscles weaken, necessitating ventilation support. Non-invasive ventilation or even tracheostomy might be considered to help with breathing.
Managing and Preventing ALS
Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy
Physical and occupational therapies play a crucial role in managing ALS. They help individuals maintain their independence, manage pain, and improve overall well-being.
Nutritional Support
Maintaining proper nutrition is vital for individuals with ALS, as muscle weakness can lead to difficulties in chewing and swallowing. Nutritional support plans are tailored to each patient’s needs.
Mind-Body Techniques
Mind-body techniques like meditation and relaxation exercises can assist in managing the emotional and psychological challenges that come with an ALS diagnosis.
Research and Future Possibilities
Investigational Treatments
Ongoing research is exploring potential treatments for ALS. Experimental approaches such as stem cell therapy and gene therapy show promise in slowing down or halting the disease’s progression.
Advancements in Genetic Studies
Genetic studies continue to uncover the complexities of ALS. Understanding the genetic underpinnings of the disease might pave the way for targeted therapies.
Living with ALS
Coping Strategies
Being diagnosed with ALS is undoubtedly overwhelming. Developing coping strategies, seeking support from loved ones, and engaging in activities that bring joy can help individuals navigate this challenging journey.
Support Networks
Support groups and organizations dedicated to ALS provide invaluable emotional support, information, and resources for individuals and their families.
Conclusion
ALS is a multifaceted disorder that affects motor neurons, leading to progressive muscle weakness and decline in quality of life. While there’s no cure, various treatments and therapies can enhance the well-being of individuals living with ALS. Ongoing research offers hope for future breakthroughs, making it crucial to continue supporting those affected by this condition.