Eczema is a complex skin condition encompassing multiple types, each with its unique features and triggers. This article delves into seven distinct eczema types, providing insights into their visual characteristics, potential causes, and ways to manage them.
Section 1: Atopic Dermatitis
**1. Introducing Atopic Dermatitis: The Most Common Eczema Type: Overview: Learn about atopic dermatitis, the prevalent form of eczema characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin patches.
**2. Visual Characteristics of Atopic Dermatitis: Recognizing the Signs: Overview: Explore the visual cues of atopic dermatitis, including red, scaly patches that commonly appear on the elbows, knees, and face.
Section 2: Contact Dermatitis
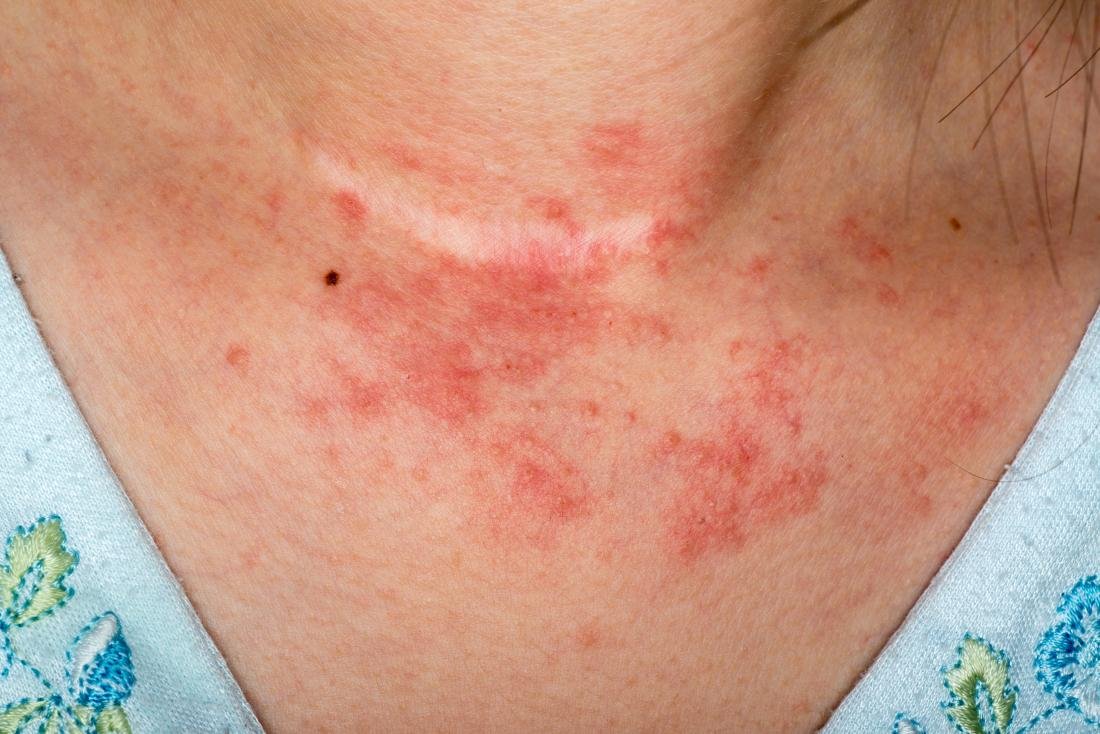
**1. Understanding Contact Dermatitis: Triggered by External Factors: Overview: Dive into contact dermatitis, which arises from exposure to irritants or allergens, causing itching, redness, and blisters.
**2. Visual Traits of Contact Dermatitis: Identifying Irritant and Allergic Reactions: Overview: Discover how contact dermatitis presents with inflamed, rash-like patches that mirror the substances triggering the reaction.
Section 3: Nummular Eczema
**1. Decoding Nummular Eczema: Discoid Patches of Irritation: Overview: Explore nummular eczema, characterized by circular or coin-shaped patches that can be intensely itchy and cause discomfort.
**2. Visual Characteristics of Nummular Eczema: Circular Patches and Their Variations: Overview: Understand how nummular eczema manifests as distinct, coin-sized patches that often appear on the arms, legs, and torso.
Section 4: Dyshidrotic Eczema
**1. Demystifying Dyshidrotic Eczema: Blisters on Fingers and Toes: Overview: Examine dyshidrotic eczema, marked by small, itchy blisters primarily on the hands and feet.
**2. Visual Attributes of Dyshidrotic Eczema: Identifying the Tiny Blisters: Overview: Learn to recognize the small, fluid-filled blisters that accompany dyshidrotic eczema and how they affect the skin’s appearance.
Section 5: Seborrheic Dermatitis
**1. Unveiling Seborrheic Dermatitis: Scalp and Skin Flakiness: Overview: Delve into seborrheic dermatitis, which often presents as flaky, oily patches on the scalp, face, and other areas rich in sebaceous glands.
**2. Visual Presentation of Seborrheic Dermatitis: Flakes and Inflammation Patterns: Overview: Explore how seborrheic dermatitis manifests with yellow or white scales and redness, affecting areas like the scalp, eyebrows, and nose folds.
Section 6: Stasis Dermatitis
**1. Understanding Stasis Dermatitis: Linked to Circulation and Fluid Buildup: Overview: Discover stasis dermatitis, occurring in areas with poor circulation and resulting in red, swollen, and itchy skin.
**2. Visual Features of Stasis Dermatitis: Redness, Swelling, and Skin Changes: Overview: Learn to identify the visual attributes of stasis dermatitis, such as inflamed, discolored skin around the ankles and lower legs.
Section 7: Neurodermatitis
**1. Exploring Neurodermatitis: Itchy Patches Due to Nerve Irritation: Overview: Examine neurodermatitis, characterized by localized patches of thickened, itchy skin triggered by nerve irritation.
**2. Visual Indications of Neurodermatitis: Scratch Marks and Lichenification: Overview: Understand how neurodermatitis manifests with raised, scaly patches and visible scratch marks, often occurring in areas the person can reach.
Conclusion: Recognizing the diverse eczema types empowers individuals to seek timely diagnosis and effective management strategies. Each type has distinct visual characteristics, triggers, and treatment approaches, fostering a comprehensive understanding of this complex skin condition.
FAQs: Q1: What is the most common type of eczema? A: Atopic dermatitis is the most prevalent form of eczema, often associated with a genetic predisposition to skin sensitivity.
Q2: Can eczema be cured? A: While eczema cannot be completely cured, effective management strategies can alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
Q3: Are the triggers for each eczema type the same? A: Triggers vary for different eczema types. Atopic dermatitis is often linked to genetics and environmental factors, while other types can be triggered by irritants, allergens, or nerve irritation.
Q4: How can I manage eczema symptoms? A: Managing eczema involves moisturizing regularly, avoiding triggers, using prescribed medications, and consulting a dermatologist for personalized guidance.
Q5: Can eczema types change over time? A: While some individuals may experience changes in the type or severity of their eczema, proper management can help control symptoms and prevent exacerbations.